
Shock wave therapy
Fast and effective pain therapy
- Unique, non-invasive (= not injuring the body) treatment of musculoskeletal pain (= pain of muscles and bones)
- Only three to four treatments are required at weekly intervals
- Treatment duration is just about 10 minutes
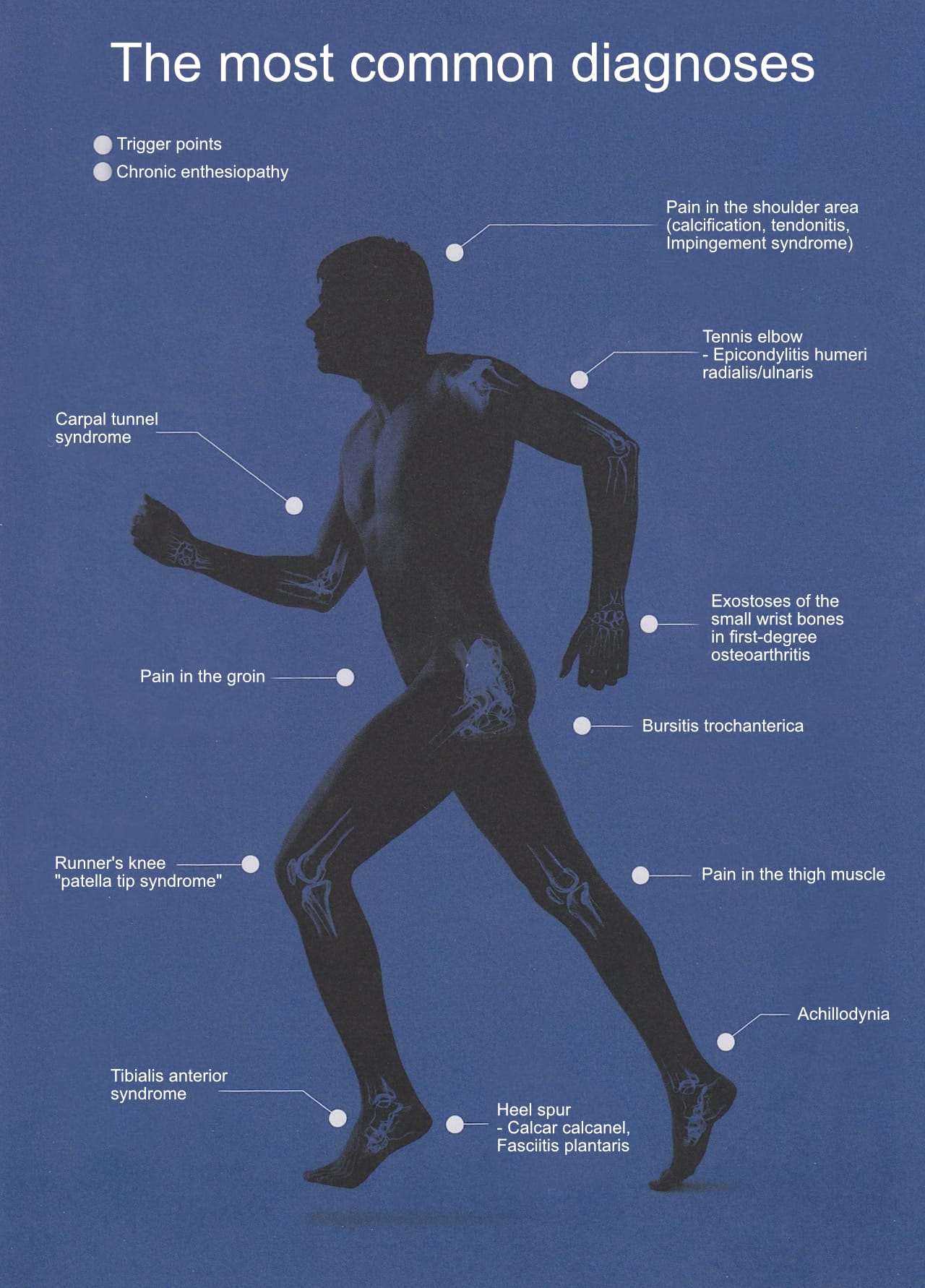
Treatment areas
- Orthopaedics
- Rehabilitation
- Sports medicine
- Maxillofacial dental medicine (CMD)
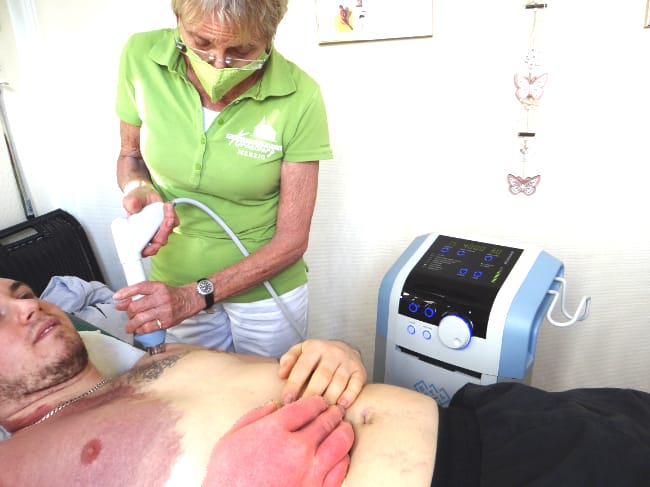
Mode of action
During treatment with shock waves, acoustic waves are transmitted into the tissue, the energy of which heals painful areas in the connective or myoskeletal tissue (= muscle and bone tissue) with sub-acute, sub-chronic and chronic conditions (= suddenly occurring, for a long time, pathological). This energy stimulates healing, regeneration and repair mechanisms of the tendons and soft tissue.
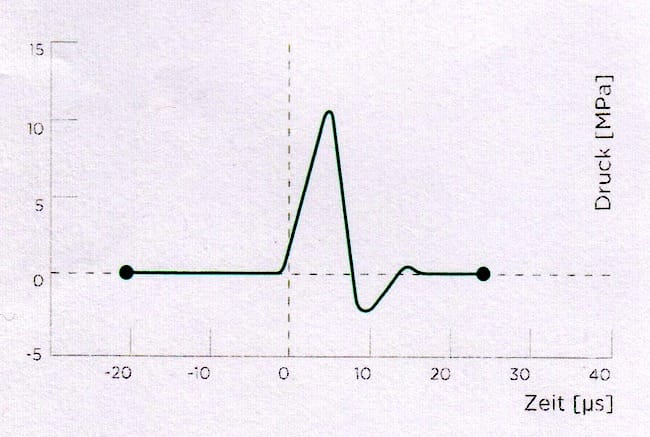
Shock waves are characterised by an abrupt increase in pressure with high amplitude and non-periodic progression.

The pneumatically generated kinetic energy of the projectile is transmitted to the transmitter at the end of the applicator.
Analgesic effect - pain relief
REDUCTION OF MUSCLE TENSION, INHIBITION OF SPASMS.
Hyperaemia is one of the main effects of shock wave therapy in the body. It results in an improved energy supply to the hypertonic (= tense) muscles and their tendons.
In addition, the pathological interaction between actin and myosin (= interaction of cells) is reduced.
This results in a reduction of muscle tension, which is often painful for the patient.

ENHANCED RELEASE OF "SUBSTANCE P".
Substance P activity (pain mediator and growth factor) leads to stimulation of afferent nociceptive fibres. It also improves the development of oedema and supports the secretion of histamines. Decreasing their concentration relieves pain in the affected area and reduces the development of oedema.
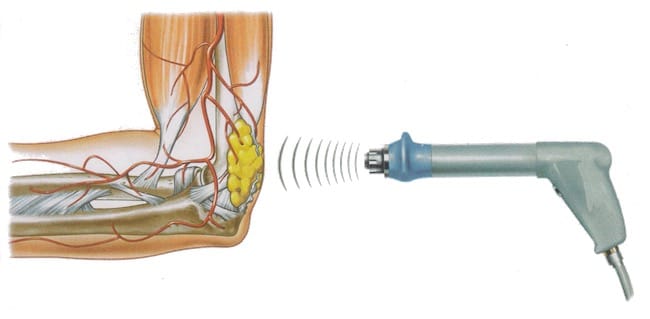
Acceleration of healing
INCREASE OF COLLAGEN PRODUCTION
The production of sufficient collagen is a necessary precondition for the tissue repair process. Shockwave therapy stimulates collagen production in deeper tissue layers.
Improved metabolism and microcirculation
Shockwave therapy accelerates the removal of nociceptive metabolites, aids oxygenation and energises damaged tissue. It promotes the removal of histamine, lactate and other nociceptive metabolic products, most of which are acidic in nature.

Restoration of mobility
Dissolution of calcified fibroblasts
Shockwave therapy dissolves the calcified fibroblasts and then triggers the biochemical decalcification of primary exostosis or secondary symptoms of arthrosis.


 DE
DE
 FR
FR